Let’s dive into one of the tiniest yet most powerful parts of your body — the anterior pituitary. This small, pea-sized gland is a hidden powerhouse that plays a significant role in almost every essential function in your body. From growth to stress response, metabolism, and even reproduction, it’s incredible how much influence this little gland has. Once you understand its role, you’ll never look at hormones the same way again!
What is the Anterior Pituitary?
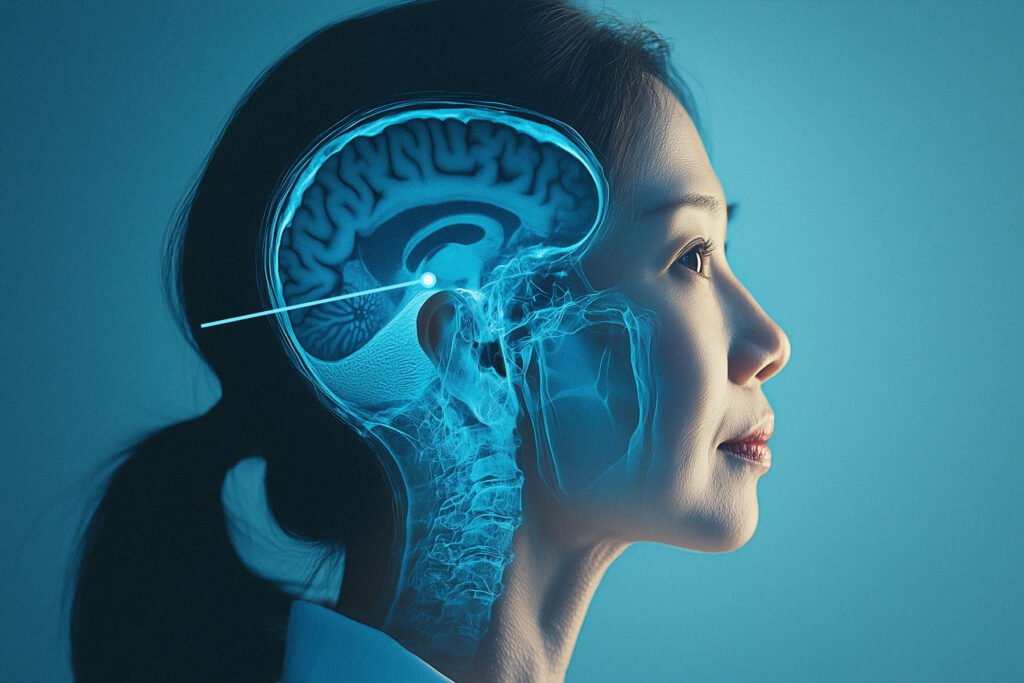
The anterior pituitary, also called the adenohypophysis, is like the CEO of your body’s “hormone company.” It’s located at the base of your brain, behind your nose, and is part of the larger endocrine system. This system is responsible for producing and releasing hormones that control many vital functions. Though small, the anterior pituitary is incredibly busy, managing multiple bodily processes by releasing crucial hormones.
The Six Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary: Your Body’s Chemical Messengers
The anterior pituitary produces six essential hormones, each responsible for specific tasks in your body. Let’s break them down:
1. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
ACTH is like your body’s stress manager. It prompts the adrenal glands to release cortisol, the well-known “stress hormone.” Whenever you feel stressed — say, during a big presentation or a challenging task — ACTH is at work, ensuring that your body has enough cortisol to handle the pressure. This hormone helps you stay alert and responsive, even in high-stress situations.
2. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
FSH plays a crucial role in reproduction. In women, it prepares eggs for ovulation, while in men, it stimulates sperm production. Without FSH, the reproductive cycle wouldn’t function as it should. This hormone ensures that each cycle is timed perfectly, allowing for fertility and reproduction.
3. Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH is another multi-tasking hormone. In women, it helps release eggs from the ovaries and initiates progesterone production. In men, it stimulates testosterone production, impacting characteristics like muscle mass and even facial hair growth. LH plays a key role in both reproductive health and general hormone balance.
4. Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
HGH is the “growth cheerleader” for your body. It helps kids grow taller and builds strong bones. In adults, it maintains muscle mass and bone health. If you’ve ever wondered why some people retain their muscle tone or heal quickly, HGH is likely doing its job behind the scenes.
5. Prolactin
Known as the “nurturing hormone,” prolactin is essential for new mothers because it stimulates breast milk production. It also influences fertility and sexual function, making it a hormone that works in multiple areas of life.
6. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
TSH directs the thyroid gland, telling it when to release its hormones. The thyroid controls metabolism, affecting how efficiently your body burns calories. If you’ve ever met someone with a fast metabolism, thank TSH for keeping their thyroid on track.
How Does the Anterior Pituitary Communicate?
The anterior pituitary doesn’t work alone. Its best friend, the hypothalamus, acts as the coordinator. The hypothalamus sends “releasing hormones” that either speed up or slow down the production of the anterior pituitary’s hormones. Imagine the hypothalamus as a team manager, ensuring that everything stays on schedule. It’s like when you get a reminder text from a friend — without it, you’d miss important cues!
Where is This All Happening?
Your pituitary gland sits in a small chamber within your skull, known as the sella turcica. This location provides a snug home for both the anterior and posterior pituitary glands. Think of them as the ultimate hormone power duo, each responsible for specific functions that keep your body balanced and healthy.

What Happens When the Anterior Pituitary Misbehaves?
While this gland is a high performer, sometimes things go awry. Here are two common issues:
- Hypopituitarism: This condition occurs when the anterior pituitary doesn’t produce enough hormones. It can lead to adrenal insufficiency (low cortisol), growth hormone deficiency, and even hypothyroidism (low thyroid function).
- Hyperpituitarism: This condition happens when the anterior pituitary produces too many hormones. It can cause issues like acromegaly, where bones grow abnormally, or Cushing’s disease, characterized by excess cortisol, leading to weight gain and fatigue.
The Role of Pituitary Tumors – Don’t Panic!
When people hear “tumor,” it’s easy to panic. But most pituitary tumors, called adenomas, are benign. These non-cancerous growths may interfere with hormone production, leading to either excess or deficiency. For example, a prolactinoma tumor can cause an overproduction of prolactin, affecting the menstrual cycle and fertility. The good news is that these tumors are usually manageable with treatment.
Real-Life Example: A Day in the Life of Your Hormones
Imagine a stressful workday. Your boss assigns a last-minute project, and you’re feeling the pressure. During this time, your hypothalamus signals the anterior pituitary to release ACTH, which then prompts your adrenal glands to produce cortisol. This stress hormone helps you stay focused, giving you the energy to power through. Once the stressful event is over, cortisol levels gradually decrease, and your body returns to a balanced state. This cycle illustrates just how vital the anterior pituitary is in managing your stress response and overall well-being.
Keeping Your Anterior Pituitary Healthy
Maintaining a healthy anterior pituitary is about taking care of your overall health. Here are some tips:
- Protect Your Head: Head injuries can disrupt pituitary function. Wear helmets when biking, buckle up in the car, and practice safe activities.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can overload the anterior pituitary. Incorporate relaxation techniques like mindfulness and deep breathing into your daily routine.
- Get Enough Sleep: Hormone production relies on rest. Ensure you get 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Final Thoughts: Respect the Power of Your Anterior Pituitary
Despite its tiny size, the anterior pituitary is the MVP of your endocrine system. It manages stress, growth, reproduction, and metabolism. By caring for your overall health, you’re supporting this small but mighty gland in performing its job. So, next time you feel stressed or experience a mood swing, remember that your anterior pituitary is working hard to keep everything in balance!







