Sleep is more than just closing your eyes and drifting into dreams; it’s a complex process intricately regulated by hormones in your body. These chemical messengers dictate when you feel sleepy, when you wake up, and even how well you rest during the night. Understanding how hormones influence your sleep cycle can empower you to take charge of your sleep quality and improve your overall well-being.
The Science Behind Sleep Hormones
The sleep-wake cycle, also known as the circadian rhythm, is largely governed by hormones that act as signals to your body. Let’s break down the key players:
1. Melatonin: The Sleep Hormone
Produced by the pineal gland in response to darkness, melatonin is the hormone that tells your body it’s time to sleep. It doesn’t “knock you out” but rather prepares your body by lowering alertness and core body temperature. Melatonin levels typically rise in the evening, peak at night, and decrease in the morning as light exposure signals your body to wake up.
2. Cortisol: The Awakening Hormone
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a counterbalancing role to melatonin. Its levels are naturally lowest at night but start to rise in the early morning, peaking around the time you wake up. This hormone gives you the energy and alertness needed to tackle the day ahead.
3. Growth Hormone: The Repair Crew
During deep sleep (primarily in Stage 3, or slow-wave sleep), the pituitary gland releases growth hormone. This hormone is essential for tissue repair, muscle growth, and overall recovery, making quality sleep crucial for physical health.
4. Estrogen and Progesterone: The Female Hormones
In women, estrogen and progesterone also play significant roles in sleep quality. Estrogen promotes REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, which is linked to dreaming and emotional regulation. Progesterone has a sedative effect, helping women fall asleep more easily. However, fluctuations in these hormones—such as during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause—can disrupt sleep patterns.
5. Testosterone: The Male Hormone
Testosterone, predominantly a male hormone but also present in women, peaks during deep sleep. Lower testosterone levels, often caused by sleep deprivation, can lead to fatigue and reduced recovery. This creates a feedback loop where poor sleep affects hormone levels, and imbalanced hormones further disrupt sleep.
6. Insulin and Leptin: Metabolic Regulators
Insulin and leptin are hormones that influence hunger and metabolism, indirectly impacting sleep. Disrupted sleep can lead to imbalances in these hormones, causing cravings and weight gain, which further interfere with sleep quality.

Hormonal Differences in Sleep Between Genders and Ages
Women
Women are more likely to experience sleep disturbances due to hormonal fluctuations. For instance:
- Menstrual Cycle: Changes in estrogen and progesterone levels during the cycle can lead to insomnia or restless sleep, especially in the days leading up to menstruation.
- Pregnancy: Rising progesterone levels in the first trimester can cause excessive daytime sleepiness, while physical discomfort and hormonal changes in the third trimester can disrupt sleep.
- Menopause: Declining estrogen levels can lead to hot flashes and night sweats, which severely impact sleep quality.
Men
Men generally have more stable hormone levels, but testosterone dips as they age or with poor sleep habits. Reduced testosterone levels can lead to fragmented sleep and a decrease in deep sleep stages, which are vital for recovery.
Children and Teenagers
In children, melatonin levels are naturally higher, helping them fall asleep early and get longer rest. However, in teenagers, melatonin production shifts later in the evening, making them “night owls.” This natural delay in sleep timing often conflicts with early school schedules, leading to chronic sleep deprivation.
How to Improve Sleep Quality Through Hormonal Balance
1. Embrace a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day reinforces your circadian rhythm. This consistency helps regulate melatonin and cortisol levels, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up refreshed. The natural sleep cycle is controlled by your pineal gland. A a tiny endocrine gland in the middle of your brain that helps regulate your body’s circadian rhythm by releasing the hormone melatonin.
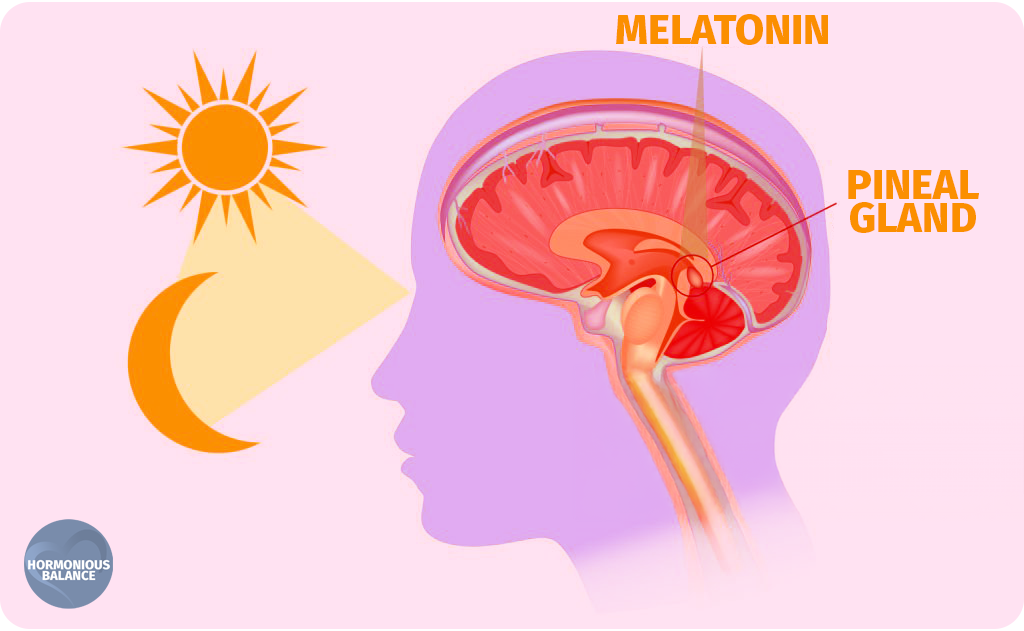
2. Optimize Your Light Exposure
- Morning Light: Get natural sunlight exposure early in the day to lower melatonin levels and boost cortisol, signaling your body to wake up.
- Evening Darkness: Minimize blue light exposure from screens at least 1–2 hours before bedtime. This allows melatonin production to ramp up naturally.
3. Manage Stress and Cortisol Levels
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, disrupting your ability to fall and stay asleep. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to lower stress and prepare your body for restful sleep.
4. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Your bedroom should be a haven for sleep. Keep it cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in blackout curtains, white noise machines, or a weighted blanket to improve your sleep quality.
5. Focus on Diet and Exercise
- Diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Include sleep-friendly foods like bananas, almonds, and turkey, which contain tryptophan, a precursor to melatonin.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid intense workouts too close to bedtime, as they can elevate cortisol levels.
6. Support Hormonal Health
- For Women: Consider supplements like magnesium or adaptogenic herbs to manage hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle or menopause.
- For Men: Ensure adequate deep sleep to maintain healthy testosterone levels.
7. Consider Professional Guidance
If sleep disturbances persist, consult a healthcare provider. Hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid dysfunction or adrenal fatigue, might require targeted treatment to restore balance and improve sleep.
The Bigger Picture: Sleep and Holistic Health
Sleep isn’t just about feeling rested—it’s a cornerstone of your overall health. Poor sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to a ripple effect on mood, metabolism, immune function, and even long-term risks like heart disease or diabetes. By prioritizing sleep hygiene and addressing hormonal health, you can unlock the full potential of your body’s natural rhythms.
Whether you’re navigating hormonal changes as a woman, striving for better recovery as a man, or supporting a teenager through their sleep struggles, understanding the role of hormones is key to unlocking restful nights. With the right knowledge and habits, you can transform your sleep and enhance your quality of life. Sweet dreams await!







